Introduction
This article introduces Entity Framework to absolute beginners. The article is meant for developers who are primarily using ADO.NET to write their data access layers. Many experienced developers will find this article very basic but since the article is written from the perspective of beginners, I've tried to keep things simple.
Background
ADO.NET is a very strong framework for data access. ADO.NET has been around since many years and there are a lot of systems running over ADO.NET. Developers who are totally oblivious to the concept of ORMs will probably be asking "What is Entity Framework? What are the benefits of using it and is it an alternative to ADO.NET?"
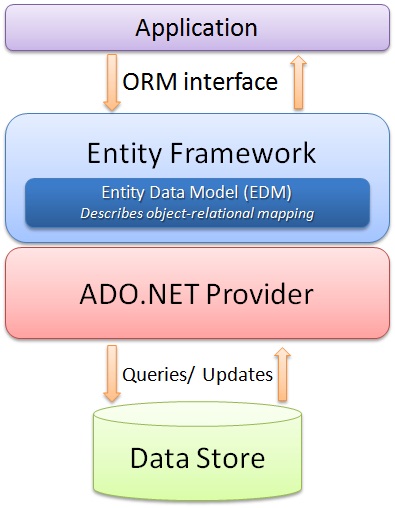
Well, to answer the first question about what is Entity Framework, Entity Framework is an Object Relational Mapper (ORM). It basically generates business objects and entities according to the database tables and provides the mechanism for:
- Performing basic CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations.
- Easily managing "1 to 1", "1 to many", and "many to many" relationships.
- Ability to have inheritance relationships between entities.
and to answer the second question, the benefits are:
- We can have all data access logic written in higher level languages.
- The conceptual model can be represented in a better way by using relationships among entities.
- The underlying data store can be replaced without much overhead since all data access logic is present at a higher level.
and finally, the last question that whether it is an alternative to ADO.NET, the answer would be "yes and no". Yes because the developer will not be writing ADO.NET methods and classes for performing data operations and no because this model is actually written on top of ADO.NET, meaning under this framework, we are still using ADO.NET. So let us look at the architecture of Entity Framework (diagram taken from MSDN):
Using the code
Let's try to understand the ease of use that Entity Framework provides by performing simple CRUD operations. Once we look at the code and how effortlessly and efficiently we can do these operations, the benefits of Entity Framework will become quite obvious.
Creating the database
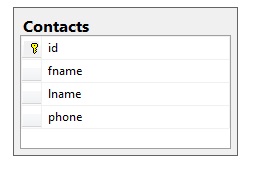
Let's have a simple database with one table. Let's create a simple table for Contacts and we will perform CRUD operations on this table.
Adding the Entity Model to the Website
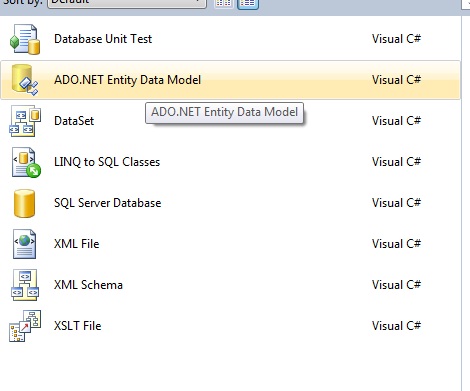
Once we have the database ready, we can add the entity model to our website. We can do this by adding an ADO.NET Entity Data Model to the website.
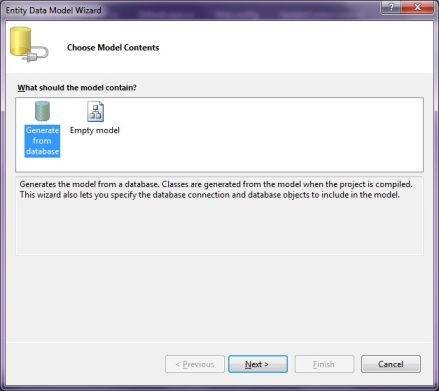
Once we select to add this data model to our website, we will have to select the approach we want to take for our Model's contents.
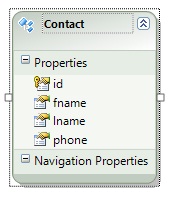
What this selection means is that we can either choose to generate the entity model from an existing database schema or we can design the entity model here and then later hook it up to the database. Since we already have the database ready, we will use the first option. Once the Model is generated, the Entity for each table is generated. The generated entity for our contact table is:
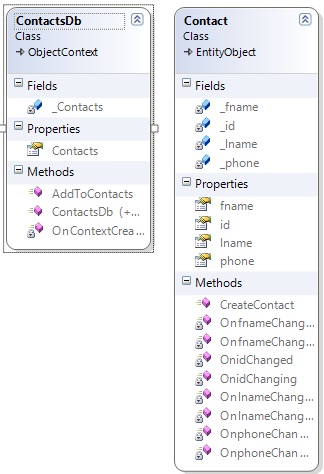
Also, the classes for performing database operations are also created. We just need to know how to use these classes to perform database operations.
Insert operation
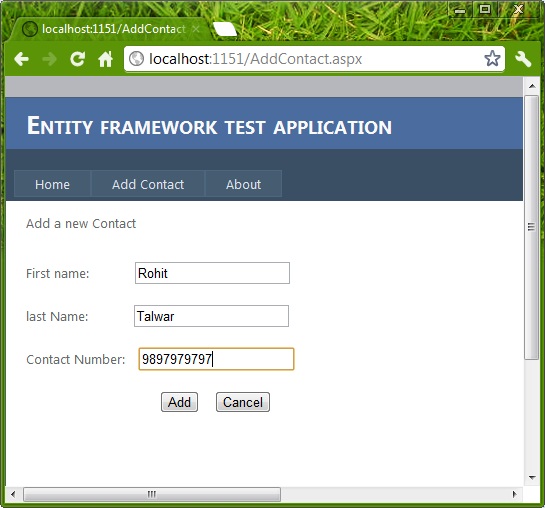
Let us create a simple page to perform an insert operation.
Now once the user chooses to insert the values into the database, the actual data operation can be performed by using the AddObject method of the Model class entity collection. The following code snippet show how to perform the insert.
Contact con = new Contact();
con.fname = TextBox1.Text;
con.lname = TextBox2.Text;
con.phone = TextBox3.Text;
ContactsDb db = new ContactsDb();
db.Contacts.AddObject(con);
db.SaveChanges();
This will insert the record into the table. You can notice the simplicity and efficiency of the code we wrote to perform the insertion.
Reading all the records
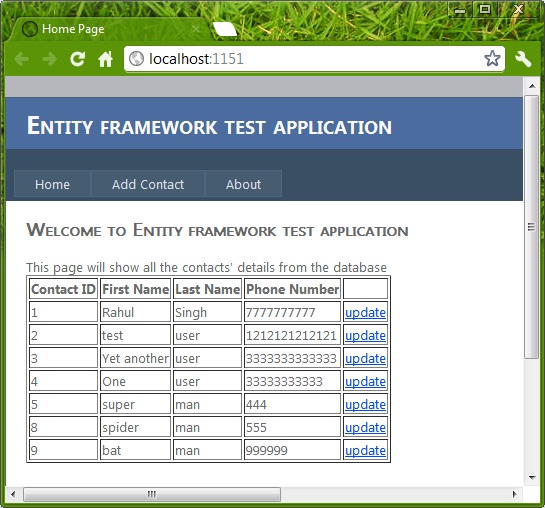
There are scenarios when we want to read all records. Let's say we are making a page that will display all the contact information in a single page.
We can retrieve the collection of Entities using the Model object to achieve this. The code snippet below will show how that can be done.
ContactsDb db = new ContactsDb();
Repeater1.DataSource = db.Contacts;
Repeater1.DataBind();
Selecting a specific record
If we want to select a specific record from the table, we can use the SingleOrDefault method on the Model's entities collection. Let's say we want the functionality of updating/deleting a record on a single page then we will first have to select the record based on the ID, then update/delete the selected record.
Selection of any particular record (Contact) based on ID can be done as:
int idToupdate = Convert.ToInt32(Request.QueryString["id"].ToString());
ContactsDb db = new ContactsDb();
Contact con = db.Contacts.SingleOrDefault(p => p.id == idToupdate);
Once this code is executed, the Contact object will contain the required values.
Updating the record
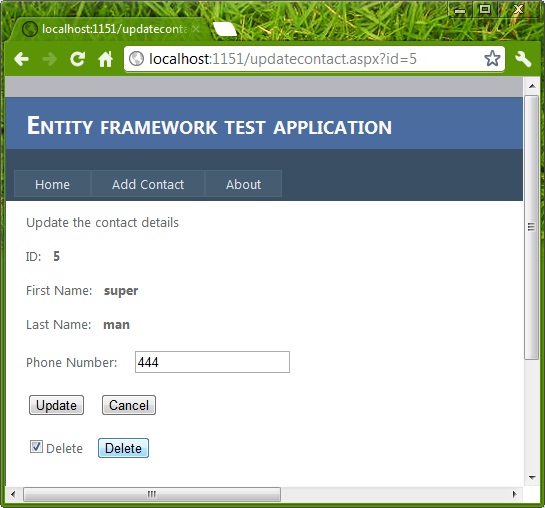
If we want to update a record, then a simple update operation can be performed as:
int idToupdate = Convert.ToInt32(Request.QueryString["id"].ToString());
ContactsDb db = new ContactsDb();
Contact con = db.Contacts.SingleOrDefault(p => p.id == idToupdate);
con.phone = TextBox1.Text;
db.SaveChanges();
Once this code executes, the value of phone number will be updated by a new value which is retrieved from TextBox1.
Deleting a record
If we want to delete a particular record then we can perform a delete operation by using the DeleteObjectfunction. The following code snippet demonstrates the same:
int idToupdate = Convert.ToInt32(Request.QueryString["id"].ToString());
ContactsDb db = new ContactsDb();
Contact con = db.Contacts.SingleOrDefault(p => p.id == idToupdate);
db.Contacts.DeleteObject(con);
db.SaveChanges();
Now that we have the basic CRUD operations performed on the database using the Entity Framework.
A note on Relationships and Lazy Loading
To understand the Entity Framework we need to understand some things like naming conventions, relationships between tables, and relationships between entities. Also, the concept of lazy loading once fully understood will give the power to the developer to use the Entity Framework efficiently.
Note: Since this is an introductory article on Entity Framework we have not discussed these things. Perhaps we will discuss them in a separate article.
Points of interest
Entity Framework has been in use for some time now. But there are many developers who are still getting started with Entity Framework. This article was meant as an overview of the Entity Framework. This should not be treated as a complete tutorial. Also, the code written is very simple and there is a lot of scope for optimization but since the idea here is to understand Entity Framework, I tried to keep the code simple and readable rather and optimal.
Note: To run the solution, please change the database path of ConnectionString in the web.config file.